Scope Measurement
Hints
Use
Holdoff to Stabilize Complex Digital Waveforms
Scope
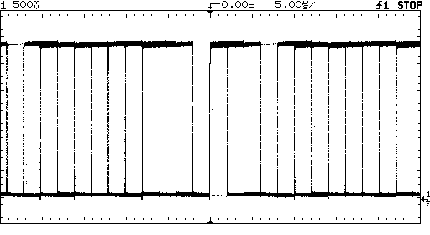
users typically start out using edge triggering. In this mode, the
scope will trigger on any edge that meets the setup criteria, for
instance any rising edge on channel 1 at 1.5 V. The trigger event
becomes the time reference for displaying the data. This presents
a problem when there are many edges at different positions in the
waveform that meet this criteria, as is the case with complex waveforms.
The scope triggers on multiple edges and overlays the waveforms
with different time references. The result is a complicated display
that looks untriggered. See Figure 1.
Figure
1
Try
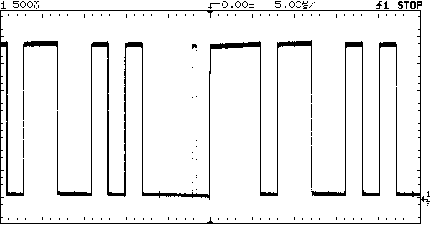
using your scopeís holdoff feature to stabilize such a waveform.
When holdoff is used, the scope triggers on the first rising edge
it sees, but then waits the holdoff time before re-arming the trigger
to look for the next trigger event. Use a holdoff time just less
than the period of the repetition of the waveform. For this example,
the holdoff time is 28 microseconds. See Figure 2. The scope now
triggers on the same edge every time, so the data has the same time
reference each time it is displayed. It is now evident that there
is an intermittent glitch.
Figure
2
|
