Scope Measurement
Hints
An
Easy Way to Isolate the Cause of Noise Problems
In
todayís digital systems, noise coupled from other parts of the system
is a common problem. Whether the noise is caused by a switching
power supply, CRT interference, or the system clock, this measurement
technique will help isolate the cause of the noise. Noise signals
are tricky to analyze on a scope. Typically the scope is triggered
on a signal other than the noise itself, since many times noise
signals are so small that it is difficult to trigger on them directly.
Figure 1 shows a noisy ground signal with the scope auto triggered.
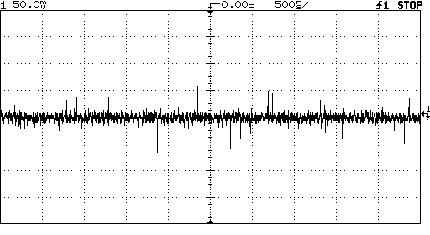
Figure
1
A
solution to this problem is to trigger on the suspected noise source.
See Figure 2. In this case, the 516 kHz clock signal was suspected.
Triggering on the clock signal (channel 2) and viewing the noisy
ground signal on channel 1 results in a trigger synchronous to the
noise. Now you can use averaging to average out the asynchronous
noise. Using this technique, itís easy to see that this noise is
indeed due to the 516 kHz clock.
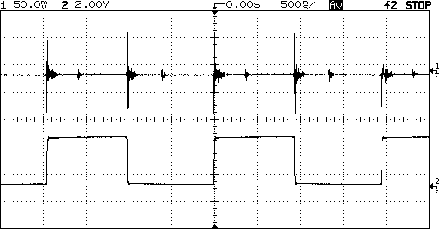
Figure
2
If
there are multiple noise sources, the same technique can be used
to isolate the noise components that are due to each noise source,
with the contributions from all other asynchronous noise sources
eliminated through averaging.
|
